[본 게시글은 고려대학교 COSE111 김승룡 교수님의 전산수학1을 듣고 정리하기 위해 작성한 글입니다.]
전산수학
1.1 Systems of Linear Equations
- Linear equation의 해
- inconsistent(해가 없다)
- consistent(해가 있다)
- uniqueness(유일성)
- Matrix
- essential information of a linear system recorded compactly in a rectangular array called matrix
- set of linear system

- coefficient matrix

- augmented matrix

- size of a matrix
- m x n ( rows and columns)
- essential information of a linear system recorded compactly in a rectangular array called matrix
- Elemantary Row Operations
- Replacement
- Interchange
- Scaling
- Row Equivalent
- two matrices are called row equivalent if there is a sequence of elemantary row operations that transform one into other.
1.2 Row reduction and Echelon Forms
- non zero row or column means a row or column that contains at least one nonzero entry
-leading entry of a row refers to the leftmost non zero entry

1.9 연습 문제 보기. 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.5 2.8
1. Echelon matrix is a matrix in echelon form
- matrix can be row reduced into many echelon forms but there is only one reduced echelon form.
- If a matrix A is row equivalent to an echeoln matrix U we call U an echelon form of A.
2. Pivot Positions
- row operations to obtain the reduced echelon form from echelon form do not change the leading entries.
- leading entries are always in the same positions in any echelon form obtained from a given matrix

- Row reduction algorithm
- step 1-4 is called the forward phase(creates a echelon form)
- step 5 is called a backward phase(creates a reduced echelon form)
- Basic Variables
- variables corresponding to pivot columns in the matrix are called basic variables
- Free Variables
- variables that are not basic variables
- example
- Fundamental questions (Existence and uniqueness)
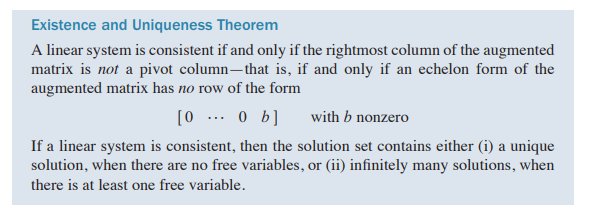
- Parametric descriptions of Solution Sets(Example)

1.3 Vector Equations
- matrix with only one column is called a Vector
- Rn n means number of rows(as vectors have only one column)
- Parallelogram Rule for Addition
- 벡터 덧셈 평행사변형법
- Linear Combinations
- y=c1v1+c2v2+c3v3+...cpvp
- Definition of Span
- zero vector is in span too.

- 헷갈릴만한 statement
- The set Span{u,v} is always visualized as a plane through the origin
- false (u might be the multiple of v)
- The set Span{u,v} is always visualized as a plane through the origin
1.4 The Matrix Equation Ax=b

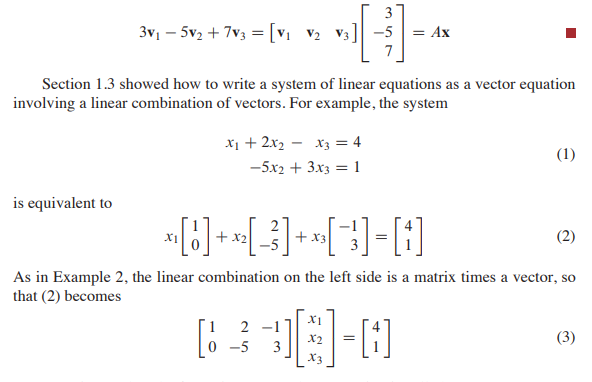



- 헷갈린 만한 부분들
- Every matrix equation Ax=b corresponds to a vector equation with the same equation set.(True)
- 1.5 Solution Sets of Linear Systems
- Homogenous system
- A system of linear equations is said to be homogenous if it can be written in the form Ax=0
- if x=0 it is called the trivial solution
- non zero vector x that satisfies Ax=0 is called a non-trivial solution

- 만약 모두 basic variable이면 trivial solution 만 존재
- Parametric vector form
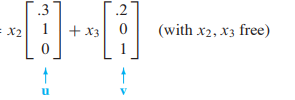
- x=p+tv
- tv는 homogeneous equation의 해와 동일.
- Solutions of Nonhomogeneous Systems

- 헷갈릴만한 문제들
- the solution set of Ax=b is the set of all vectors of the form w=p+tv, where tv is any solution of the equation Ax=0
- 거짓. 해가 없을 수도...
- The equation Ax=b is homogeneous if the zero vector is the solution
- YES!!!
- Ax=b 해가 존재하려면 모든 row에 피봇 포지션
- Ax=0이 non trivial solution 존재하려면 최소 한개의 free variable (pivot column 아닌게 존재해야됨)

- the solution set of Ax=b is the set of all vectors of the form w=p+tv, where tv is any solution of the equation Ax=0
1.7 Linear Indepence





ex)
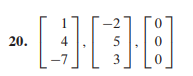
- linearly dependent

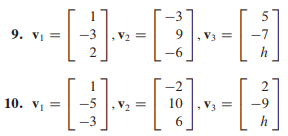
- span 이랑 linearly dependent 구분하기
- span은 v1,v2 연산 결과가 v3
- linear independent 는 v1,v2,v3 연산결과가
- linearly dependent 라고 해서 모두 다른 벡터의 연산으로 나타낼 수 있는 것은 아님.(c가0인경우)
- ex)

- 헷갈릴만한 문제들
- zero vector 경우가 있기에 거짓.



1.8 Introduction to Linear Transformations

- domain: Ax=b에서 x
- codomain: Ax=b에서 b
- image: the vector T(x) in Rm.
- range: the set of all image of x
- linear transformation

1.9 The Matrix of a Linear Transformation
- A is called the standard matrix for the linear transformation T
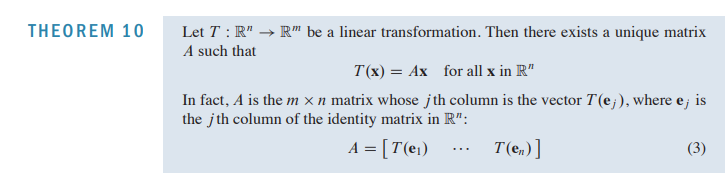
- the columns if the standard matrix for a linear transformation from Rn to Rm are the images of the columns of the nxn matrix.
![onto is same with existence question]

onto is same with existence question
- onto 이면 Rm을 span 해야됨
- span 하려면 모든 b에 대하여 성립
- every row에 pivot

one to one is same with the uniqueness question
False(모든 b가 x에 의해 결정되는 것이 중요)


증명) p이면 q이다, !p 이면 !q이다 쓰기
- one to one 이면 independent
- independent는 dependent 여부 따지기랑 동일
- free variable 존재하나?

(25-28번)예의주시하기!
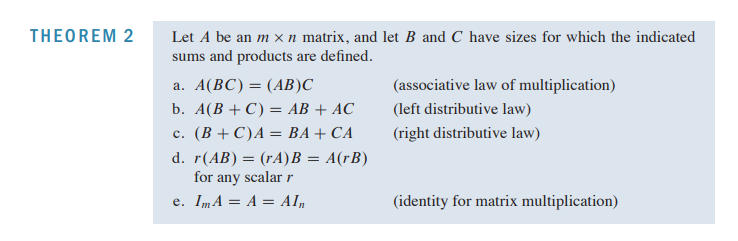
2.1 Matrix Operation
- diagonal entries
- matrix[i]j
- Equal matrix
- size가 같고 모든 칼럼이 동일
- Matrix Multiplication


2.2 The Inverse of a Matrix
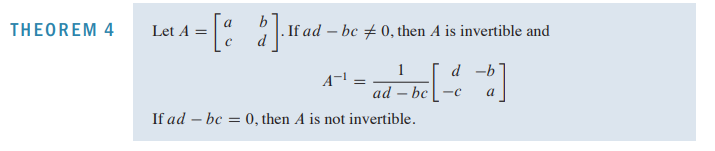
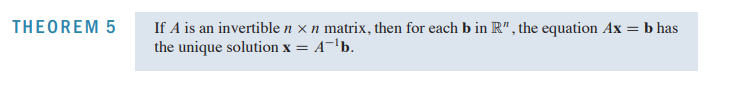
- Elementary matrix
- one that is obtained by performing a single elementary operation on an identity matrix
- Each elementary matrix is invertible



2.3 Characterizations of Invertible Matrices
- Invertible Linear Transformations

2.5 Matrix Factorizations
- The LU Factorization


2.8 Subspaces of Rn
- Definition

- closed under addition and multiplication
- zero vector도 subspace
- zero subspace
- column space

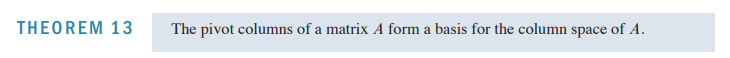
## 2.8 subspaces of Rn
dimension: 하나의 subspace를 이루는 basis의 개수

rank: column space의 basis 개수 (pivot의 개수와 같음)
- pivot column이 column space의 basis를 결정하기 때문



hint) Nul A는 Ax=0의 해
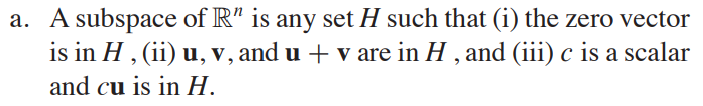

- 정답 공개c. Null space에서는 변수의 개수만큼의 subspace에 들어가 있음!
- a.거짓(모든 벡터에 대해 라는 말이 없음)
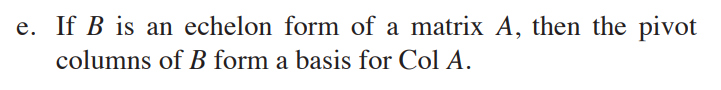
- 정답 공개
- dependent 여부는 결정 되지만, 벡터가 변화하기 때문에, Col A가 아닌 Col B의 것이다. (Col A ≠ Col B)
- 참고

2.9 Dimension and Rank

False
(subspace의 정의:zero vector가 포함 되어야 함)
6.1 Inner product, length, orthogonality




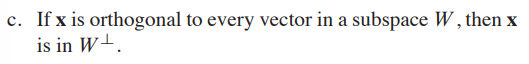

- 정답
- 둘 다 true!!

거짓!!c가 0일 수도 있답니다!
6.2 Orthogonal sets

증명 c1v1+c2v2….cnvn=0 에다가 v1내적하기!



모든 orthogonal set가 linearly independent 한 것은 아님!(zero vector 때문!!)
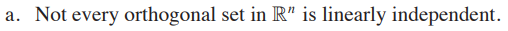
- 정답 공개
- 거짓{0,0,0,0,0}도 orthogonal 하다. 그런데 linearly dependent 함
6.3 Orthogonal Projections

6.4 The GRAM-SCHMIDT PROCESS

v1,v2,v3가 zero vector일수도 있음
6.5 LEAST-SQUARES PROBLEMS



사고의 순서: b→c→a 순서!
Ax=0이 해가 trivial 함
A^tA 해가 independent 함!
invertible 하니까 해가 유일!
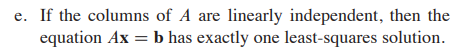
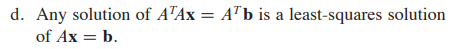


정의 읽기!
이 문제정말정말 중요!!!

//closest to b는 b(hat)…근이 아니다!

A가 invertible 해야지 성립함!
5.1 EIGENVECTORS AND EIGENVALUES

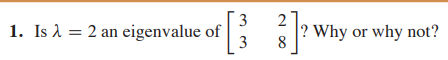
non zero vector 말고도 해를 가지느냐?
dependent 한 지를 따져야함!.
free variable이 하나라도 있어야됨!

Ax=λx를 만족하는 λ를 eigenvalue라함 non trivial solution을 의미하기에 x는 non zero 이어야 하지만, 저 식을 만족하기만 하면 되기에 λ는 0이어도 상관이 없음.

Ax=λx에서 λ가 0이고 eigen value 이면 non triavial 솔루션이 존재하고, Ax=0 의 해가 유일하지 않으므로, dependent, not invertible 함!

5.3 Diagonalization

7.1 Symmetric Matrix

A transpose는 A 이므로 A는 symmetric함!symmetric 해야 orthogonally diagonalize 할 수 있음!
- symmetric 한지 체크부터 하기 (orthogonally diagonalize 하기 전에!)
- diagonalization( decomposing eigen value)
- 첫번째 단계에서는 eigen value 를 구하는 게 최우선임
- 다른 eigen value 라면 서로 orthogonal 하지만, 같은 eigen value 아래에서는 그렇지 않으므로, 그램 슈미트 를 써준다.
- orthogonal matrix는 orthonormal sets들로 이루어져 있으므로, generalize를 해줘야 한다!.
- Symmetric Matrix의 특징들
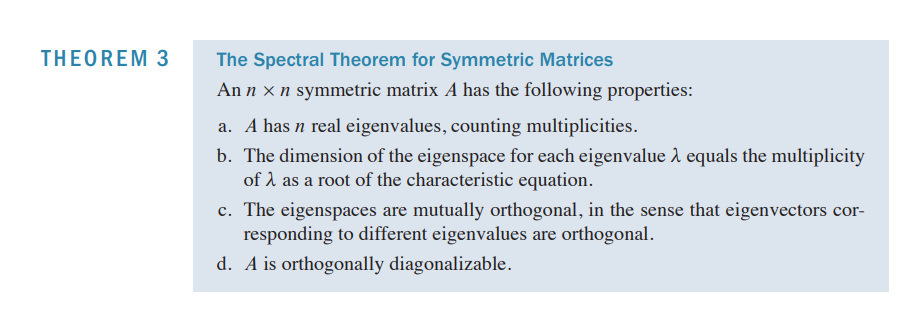
- b. characteristic equation에서 특정 eigenvalue의 거듭제곱 수 만큼의 basis가 형성됨 (dimension).
